A) 0.75 and the multiplier is 1 1/3.
B) 0.75 and the multiplier is 4.
C) 0.25 and the multiplier is 1 1/3.
D) 0.25 and the multiplier is 4.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the MPC is 0.60.Assume there are no crowding out or investment accelerator effects.If the government increases expenditures by $200 billion,then by how much does aggregate demand shift to the right? If the government decreases taxes by $200 billion,then by how much does aggregate demand shift to the right?
A) $300 billion and $180 billion
B) $300 billion and $300 billion
C) $500 billion and $300 billion
D) $500 billion and $500 billion
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
During recessions,unemployment insurance payments tend to rise.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose aggregate demand shifts to the left and policymakers want to stabilize output.What can they do?
A) repeal an investment tax credit or increase the money supply
B) repeal an investment tax credit or decrease the money supply
C) institute an investment tax credit or increase the money supply
D) institute an investment tax credit or decrease the money supply
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to simplify the equation for the multiplier to its familiar,relatively simple form,we make use of the
A) assumption that increases in government purchases have no effect on consumer spending.
B) assumption that the feedback effects associated with changes in government purchases become negligible after two or three rounds of spending have occurred.
C) empirical evidence that points to a value of aboutfor the MPC.
D) fact that the multiplier effect is represented by an infinite geometric series.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sometimes,changes in monetary policy and/or fiscal policy are intended to offset changes to aggregate demand over which policymakers have little or no control.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,if the quantity of money demanded is greater than the quantity supplied,then the interest rate will
A) increase and the quantity of money demanded will decrease.
B) increase and the quantity of money demanded will increase.
C) decrease and the quantity of money demanded will decrease.
D) decrease and the quantity of money demanded will increase.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the marginal propensity to consume is 6/7,then the multiplier is 7.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Automatic stabilizers
A) increase the problems that lags cause in using fiscal policy as a stabilization tool.
B) are changes in taxes or government spending that increase aggregate demand without requiring policy makers to act when the economy goes into recession.
C) are changes in taxes or government spending that policy makers quickly agree to when the economy goes into recession.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The change in aggregate demand that results from fiscal expansion changing the interest rate is called the
A) multiplier effect.
B) crowding-out effect.
C) accelerator effect.
D) Ricardian equivalence effect.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to a 2009 article in The Economist,the multiplier effect and crowding-out effect would exactly offset each other when the economy is
A) operating at full capacity.
B) in recession.
C) experiencing zero inflation.
D) experiencing high rates of inflation.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run,
A) the price level alone adjusts to balance the supply and demand for money.
B) output responds to changes in the aggregate demand for goods and services.
C) changes in the money supply cause a proportional change in the price level.
D) increases in the money supply shift the aggregate supply curve causing output to rise.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-6.On the left-hand graph,MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money;on the right-hand graph,AD represents aggregate demand.The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
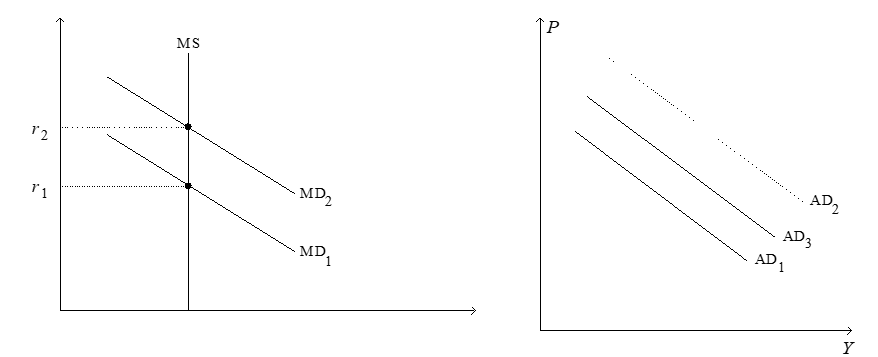 -Refer to Figure 21-6.Suppose the multiplier is 3 and the government increases its purchases by $25 billion.Also,suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out;the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out.Finally,assume the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $30 billion.The extent of crowding out,for any particular level of the price level,is
-Refer to Figure 21-6.Suppose the multiplier is 3 and the government increases its purchases by $25 billion.Also,suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out;the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out.Finally,assume the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $30 billion.The extent of crowding out,for any particular level of the price level,is
A) $25 billion.
B) $30 billion.
C) $45 billion.
D) $60 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To reduce the effects of crowding out caused by an increase in government expenditures,the Federal Reserve could
A) increase the money supply by buying bonds .
B) increase the money supply by selling bonds.
C) decrease the money supply by buying bonds
D) increase the money supply by selling bonds .
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2009 article in The Economist noted that some studies have provided evidence indicating that multipliers are
A) smaller in closed economies than in open economies.
B) larger in closed economies than in open economies.
C) smaller in capitalist economies than in socialist economies.
D) larger in capitalist economies than in socialist economies.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following cases would the quantity of money demanded be largest?
A) r = 0.03,P = 1.2
B) r = 0.03,P = 1.3
C) r = 0.04,P = 1.2
D) r = 0.05,P = 0.9
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest-rate effect
A) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services supplied.
C) is responsible for the downward slope of the money-demand curve.
D) is the least important reason,in the case of the United States,for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy
A) can be implemented quickly and most of its impact on aggregate demand occurs very soon after policy is implemented.
B) can be implemented quickly,but most of its impact on aggregate demand occurs months after policy is implemented.
C) cannot be implemented quickly,but once implemented most of its impact on aggregate demand occurs very soon afterward.
D) cannot be implemented quickly and most of its impact on aggregate demand occurs months after policy is implemented.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the money-supply curve would shift if the Fed
A) engaged in open-market transactions.
B) changed the discount rate.
C) changed the reserve requirement.
D) did any of the above.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the opportunity cost of holding money is
A) the interest rate on bonds.
B) the inflation rate.
C) the cost of converting bonds to a medium of exchange.
D) the difference between the inflation rate and the interest rate on bonds.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 451
Related Exams