A) relevancy frontier.
B) knowledge gap.
C) information asymmetry.
D) information equilibrium.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there are 3 possible outcomes to a vote: A, B, and C. If voters prefer A to B, B to C, and C to A, which of the following concepts are violated?
A) Transitivity
B) Arrow's impossibility theorem
C) Median voter theorem
D) None of the above concepts are violated.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If A is preferred to B and C is preferred to D, then B must be preferred to C to satisfy transitivity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person who makes decisions that are "merely good enough" is called a(n)
A) optimizer.
B) rational person.
C) satisficer.
D) maxi-minimizer.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists use basic psychological insights in the field of study called
A) psychological economics.
B) transitional economics.
C) behavioral economics.
D) social economics.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of screening?
A) a man buys an expensive birthday present for his girlfriend
B) an insurance company offers a policy with a high deductible
C) the seller of a used motorcycle knows more about its true condition than a prospective buyer
D) society supports long prison terms for corporate criminals
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-20
The table below shows the preferred city budget (in millions) for
in the city of Springfield. 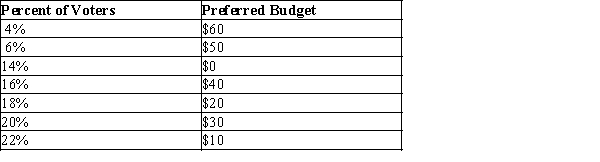 -Refer to Table 22-20. In an election, each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget. Using this information, what is the most preferred budget of the median voter?
-Refer to Table 22-20. In an election, each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget. Using this information, what is the most preferred budget of the median voter?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $40
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mother gives her teenage daughter two choices: spend 20 minutes cleaning her room today or spend 25 minutes cleaning her room tomorrow. The same mother gives her same daughter two additional choices: clean out the garage for 20 minutes next Tuesday or 25 minutes next Wednesday. According to economic theory,
A) if the daughter chooses to procrastinate, she is behaving irrationally.
B) the daughter will likely choose to clean out her room tomorrow but clean out the garage next Tuesday.
C) the daughter will likely choose to clean out her room tomorrow and clean out the garage next Wednesday.
D) if the daughter chooses to procrastinate, she is exhibiting satisficing behavior.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Arrow's impossibility theorem states that the majority rule fails to produce transitive preferences for society.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) An example of adverse selection is man who tries to sell his used car without disclosing that it needs a new transmission.
B) The "invisible hand" of a free market will always fix the problems of adverse selection and moral hazard.
C) An employer may try to prevent a moral hazard problem by paying her workers an efficiency wage.
D) One interpretation of gift giving is that it reflects asymmetric information and signaling.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the voters in a small country are choosing between two options, A and B. After the voting is complete it is discovered that option A received 100% of the votes with option B receiving no votes. After the vote, however, the country's leader decides that option B is better for the people and implements B rather than A. The voting system in this country fails which of Arrow's properties of a desirable voting system?
A) unanimity
B) transitivity
C) independence of irrelevant alternatives
D) No dictators
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Signaling is an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informed party to reveal information.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-19
The 600 voters of Appleton are deciding by majority rule how much to spend on a new library.  -Refer to Table 22-19. The median voter prefers to spend
-Refer to Table 22-19. The median voter prefers to spend
A) $2 million.
B) $3 million.
C) $3.5 million.
D) $4 million.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An insurance company that writes automobile policies tries to separate safe drivers from risky drivers by offering policies that feature different deductibles and different premiums. This practice is best described as an example of
A) screening.
B) behavioral economics.
C) monitoring.
D) signaling.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Condorcet explained his paradox in a 1951 book called Social Choice and Individual Values.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a principal-agent relationship?
A) a soccer player and her coach
B) a man and his neighbor
C) an construction worker and his foreman
D) a driver and her insurance agent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his 1951 book Social Choice and Individual Values, Arrow's perfect voting system satisfies all of the following properties except
A) unanimity.
B) transitivity.
C) reflexivity.
D) independence of irrelevant alternatives.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-5
The citizens of Anytown will decide whether to build a new library, a recreation center, or an arena. Exactly one of the three choices will prevail, and the choice will be made by way of pairwise voting, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The preferences of the voters are summarized in the table below. 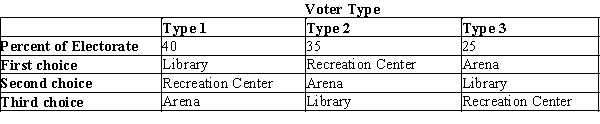 -Refer to Table 22-5. If (1) the first vote pits "library" against "recreation center," and (2) the second vote pits "arena" against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
-Refer to Table 22-5. If (1) the first vote pits "library" against "recreation center," and (2) the second vote pits "arena" against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
A) "Library" wins the first vote and "library" wins the second vote, so they build a library.
B) "Library" wins the first vote and "arena" wins the second vote, so they build an arena.
C) "recreation center" wins the first vote and "recreation center" wins the second vote, so they build a recreation center.
D) "recreation center" wins the first vote and "arena" wins the second vote, so they build an arena.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A driver knows more than his auto insurer about how cautiously he drives. This is an example of
A) a hidden action.
B) a hidden characteristic.
C) adverse selection.
D) the Condorcet Paradox.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the moral-hazard problem.
B) Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the adverse-selection problem.
C) Hidden actions are associated with the moral-hazard problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the adverse-selection problem.
D) Hidden actions are associated with the adverse-selection problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the moral-hazard problem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 461
Related Exams