B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-22
The town of Fairview is considering a renovation to the high school. The voters in Fairview have different preferences on the budget for the renovation as displayed below. 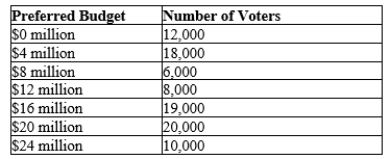 -Refer to Table 22-22. If there is a vote between a budget of $16 million and $20 million and voter vote for the budget nearest their preferred budget, then the median voter will vote to spend
-Refer to Table 22-22. If there is a vote between a budget of $16 million and $20 million and voter vote for the budget nearest their preferred budget, then the median voter will vote to spend
A) $16 million and the voting outcome will be $16 million.
B) $16 million and the voting outcome will be $20 million.
C) $20 million and the voting outcome will be $20million.
D) $20 million and the voting outcome will be $20 million.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When asked to give a range for the height of the tallest mountain in North America such that people were 90 percent confident the true number falls within it, most people gave ranges that were
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An example of an information asymmetry is when a worker knows more than his employer about his work effort.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One property of Kenneth Arrow's "perfect" voting system is that the ranking between any two outcomes A and B should not depend on whether some third outcome C is also available. Arrow called this property
A) transitivity.
B) pairwise perfection.
C) independence of irrelevant alternatives.
D) irrelevance of social choices.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Based on studies of human decision making, many people care more about the fairness of a game than about their personal winnings.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Signaling is an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informed party to reveal information.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Studies of human decision-making show that
A) firms are less likely to maximize profits than consumers are to maximize utility.
B) firms are more likely to maximize profits than consumers are to maximize utility.
C) people are irrational more often than they are rational.
D) people are reluctant to change their minds.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-2
Three longtime friends-Allen, Brian, and Cody-are deciding how they will spend their Sunday afternoon. They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, play golf, or go to a baseball game. They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their afternoon, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below. 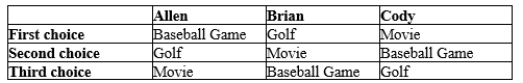 -Refer to Table 22-2. Which of the following statements is correct?
-Refer to Table 22-2. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) In a pairwise election, "movie" beats "golf."
B) In a pairwise election, "golf" beats "baseball game."
C) In a pairwise election, "baseball game" beats "movie."
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-6  -Refer to Table 22-6. The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. In pairwise majority voting in which voters choose first between A and B and then choose between the winner of the first vote and C,
-Refer to Table 22-6. The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. In pairwise majority voting in which voters choose first between A and B and then choose between the winner of the first vote and C,
A) outcome A will win the election.
B) outcome B will win the election.
C) outcome C will win the election.
D) the outcome of the election cannot be determined with the given information.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements captures the meaning of transitivity of preferences?
A) If A is preferred to B, then B is less preferred than A.
B) If A is preferred to B, and B is preferred to C, then A is preferred to C.
C) If A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C, then the preference for A over B is stronger than the preference for B over C.
D) If A is preferred to C, then there exists B such that A is preferred to B and C is preferred to A.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The median voter
A) is the voter exactly in the middle of the distribution.
B) is the voter whose preferred outcome beats any other proposal in a two-way race.
C) always has more than half the votes on his side in a two-way race.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Informational asymmetry is a difference in
A) efficiency.
B) equality.
C) relevant knowledge.
D) signaling.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) An example of adverse selection is man who tries to sell his used car without disclosing that it needs a new transmission.
B) The "invisible hand" of a free market will always fix the problems of adverse selection and moral hazard.
C) An employer may try to prevent a moral hazard problem by paying her workers an efficiency wage.
D) One interpretation of gift giving is that it reflects asymmetric information and signaling.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You own an ice cream store and are concerned that an employee may be giving generous scoops to friends and relatives and smaller scoops to some other customers. This may be reducing sales. In this example, you are the
A) principal and the your employee is the agent.
B) agent and the your employee is the principal.
C) signaler and the your employee is the screener.
D) screener and the owner of the coffee ship is the signaler.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-17 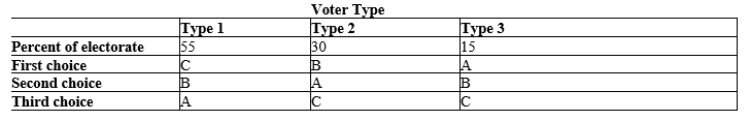 -Refer to Table 22-17. The table shows the preferences of three types of voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. The table also shows the percentage of voters of each type. Based on this information, which voter type is the median voter?
-Refer to Table 22-17. The table shows the preferences of three types of voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. The table also shows the percentage of voters of each type. Based on this information, which voter type is the median voter?
A) Type 1
B) Type 2
C) Type 3
D) The median voter cannot be determined without knowing the pair of outcomes from which the voters will be choosing.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-9 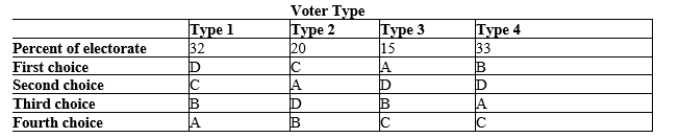 -Refer to Table 22-9. The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: A, B, C, and D. In addition, the table shows the percentage of voters of each type. Suppose that, for some reason, D is eliminated as a possible option. Using a Borda count election, with 3 points for the best choice, 2 points for the second best choice, and 1 point for the last choice, which outcome would win this election?
-Refer to Table 22-9. The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: A, B, C, and D. In addition, the table shows the percentage of voters of each type. Suppose that, for some reason, D is eliminated as a possible option. Using a Borda count election, with 3 points for the best choice, 2 points for the second best choice, and 1 point for the last choice, which outcome would win this election?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) There would be a three-way tie.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adverse selection may lead to
A) owners of used cars choosing to keep them rather than sell them at the low price that skeptical buyers are willing to pay.
B) wages being stuck above the level that balances supply and demand, resulting in unemployment.
C) buyers with low risk choosing to remain uninsured because the policies they are offered fail to reflect their true characteristics.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People interpret evidence to confirm beliefs they already hold. This statement is an example of which of the following systematic mistakes that people make?
A) people are overconfident
B) people give too much weight to a small number of vivid observations
C) people are reluctant to change their minds
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two major problems caused by asymmetric information are the moral-hazard problem and the principal-agent problem.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 361 - 380 of 461
Related Exams