A) private goods and common resources.
B) club goods and public goods.
C) common resources and public goods.
D) private goods and club goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) A free rider is a person who benefits from something for which he or she does not have to pay.
B) The creation of general knowledge is a public good.
C) The Tragedy of the Commons illustrates the underuse of a common resource.
D) A gasoline tax is an imperfect solution to the problem of traffic congestion on public roads.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When something of value has no price attached to it,
A) externalities will be present.
B) production of the product has no cost.
C) government should not intervene to produce the product.
D) private companies will eventually produce the product, and the good will no longer be free.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that you want to put on a fireworks display in your hometown of 1,000 people this July.The cost of the display is $6,000,and each person values the display at $5.After a month,you have only sold 50 tickets at $5 each.The result is that
A) the local government should put on the display, but you should not.
B) you should still put on the display, but the local government should not.
C) neither you nor the local government should put on the display.
D) either you or the local government should put on the display.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The goal of requiring licenses for hunting and fishing is
A) to reduce the use of a common resource.
B) to ensure that the people hunting and fishing are qualified.
C) to generate revenue for the government.
D) to monitor compliance with federal gun laws.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most goods in the economy are
A) club goods.
B) common resources.
C) public goods.
D) private goods.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
You and your friends watch a movie in your bedroom.For you and your friends,the enjoyment that you get from watching the movie is not rival in consumption.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A free-rider is someone who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the value of a human life is calculated according to the economic contribution a person makes to society (as reflected in her income-earning potential) ,the troubling implication is that
A) it is possible for a retired or disabled person to have no value to society.
B) economists are more valuable than entrepreneurs.
C) retired people who volunteer in their communities are more valuable than physicians.
D) all workers have equal value.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11-5
A small strip mall contains four retail stores, and crime has recently been on the increase in the neighborhood of the strip mall. The owners of the four stores - Stores A, B, C, and D - are considering contributing to a pool of money that will be used to hire up to 4 security guards. The table represents their willingness to pay, that is, the maximum amount that each store owner is willing to contribute, per day, to hire each security guard.
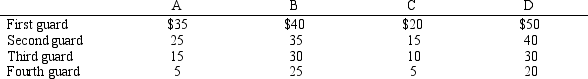 -Refer to Table 11-5.Suppose the cost to hire each individual guard is $130 per day.How many guards should be hired to maximize the total surplus of the four store owners?
-Refer to Table 11-5.Suppose the cost to hire each individual guard is $130 per day.How many guards should be hired to maximize the total surplus of the four store owners?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most lighthouses are operated by the government because
A) of the free-rider problem.
B) lighthouses are no longer valued by society.
C) most lighthouses are only tourist attractions in state and national parks.
D) shipping companies would not be able to afford maintenance fees for lighthouses.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the least regulated common resources today is
A) state parks.
B) the ocean.
C) forest preserves.
D) the Great Lakes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S.military defends Jacob from foreign attackers.The fact that Jacob enjoys this protection does not detract from others Americans' enjoyment of it.For this reason,we say that national defense is
A) excludable.
B) not excludable.
C) rival in consumption.
D) not rival in consumption.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The overuse of a common resource relative to its economically efficient use is called
A) the free rider problem.
B) the Tragedy of the Commons.
C) a public good.
D) cost-benefit analysis.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four friends decide to meet at a Chinese restaurant for dinner.They decide that each person will order an item off the menu,and they will share all dishes.They will split the cost of the final bill evenly among each of the people at the table.A Tragedy of the Commons problem is likely for each of the following reasons except
A) each person has an incentive to eat as fast as possible since their individual rate of consumption will not affect their individual cost.
B) there is an externality associated with eating the food on the table.
C) when one person eats, he may not take into account how his choice affects his friends.
D) each dish would be both excludable and rival in consumption.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using a toll to reduce traffic when congestion is greatest is an example of a
A) regulation solution.
B) command-and-control policy.
C) corrective tax.
D) Coase theorem solution.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A variable toll on a road in Washington reached a high during the evening rush hour of $5.75.This toll bought the drivers who paid it a 27 minute time savings.Which of the following is correct?
A) For some consumers, the toll was less than the opportunity cost of the time they would have spent in traffic.
B) For some consumers, the toll was more than the opportunity cost of the time they would have spent in traffic.
C) No consumers would find this toll worth the time saved in traffic.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pizza is
A) excludable and rival in consumption.
B) excludable and nonrival in consumption.
C) nonexcludable and rival in consumption.
D) nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A good that is rival in consumption is one that someone can be prevented from using if she did not pay for it.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In determining whether and how much of a public good to provide,cost-benefits analysts use the same type of price signals for public goods as are readily available for private goods.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 301 - 320 of 349
Related Exams