A) the marginal rate of substitution.
B) transitivity.
C) indifference curves bowing inward.
D) They do not violate any properties of indifference curves.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Giffen good is a good for which
A) an increase in the price raises the quantity demanded.
B) the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C) an increase in the price decreases the quantity demanded.
D) Both a) and b) are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer's optimal choice occurs when the
A) consumer's valuation of the two goods equals the market's valuation of the two goods.
B) consumer minimizes her expenditures.
C) consumer attains the highest indifference curve.
D) consumer's valuation of the two goods exceeds the market's valuation of the two goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Karen,Tara,and Chelsea each buy ice cream and paperback novels to enjoy on hot summer days.Ice cream costs $5 per gallon,and paperback novels cost $8 each.Karen has a budget of $80,Tara has a budget of $60,and Chelsea has a budget of $40 to spend on ice cream and paperback novels.Who can afford to purchase 5 gallons of ice cream and 8 paperback novels?
A) Karen, Tara, and Chelsea
B) Karen only
C) Tara and Chelsea but not Karen
D) none of the women
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-5
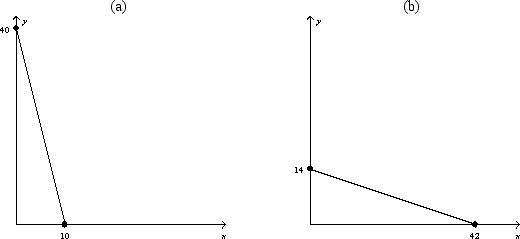 -Refer to Figure 21-5.Assume that a consumer faces the budget constraint shown in graph (a) in January and the budget constraint shown in graph (b) in February.If the consumer's income has remained constant,what has happened to prices between January and February?
-Refer to Figure 21-5.Assume that a consumer faces the budget constraint shown in graph (a) in January and the budget constraint shown in graph (b) in February.If the consumer's income has remained constant,what has happened to prices between January and February?
A) The price of X has fallen, but there could not have been a change in the price of Y.
B) The price of Y has fallen, but there could not have been a change in the price of X.
C) The price of X has fallen, and the price of Y has risen.
D) The price of Y has fallen, and the price of X has risen.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indifference curves graphically represent
A) an income level sufficient to allow an individual to achieve a given level of satisfaction.
B) the constraints faced by individuals.
C) an individual's preferences.
D) the relative price of commodities.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the consumer's optimum
A) the budget constraint will have a slope of MUx/Px.
B) it is still possible for the consumer to increase his consumption of both goods.
C) the indifference curve will intersect the budget constraint at the midpoint of the budget constraint.
D) the slope of the indifference curve is equal to the slope of the budget constraint.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect complements,the indifference curves are
A) positively sloped.
B) negatively sloped.
C) straight lines.
D) right angles.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-19
The following graph illustrates a representative consumer's preferences for marshmallows and chocolate chip cookies:
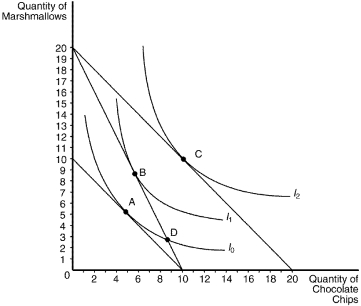 -Refer to Figure 21-19.Assume that the consumer has an income of $40,the price of a bag of marshmallows is $2,and the price of a bag of chocolate chips is $2.The optimizing consumer will choose to purchase which bundle of marshmallows and chocolate chips?
-Refer to Figure 21-19.Assume that the consumer has an income of $40,the price of a bag of marshmallows is $2,and the price of a bag of chocolate chips is $2.The optimizing consumer will choose to purchase which bundle of marshmallows and chocolate chips?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a property of a typical indifference curve?
A) upward sloping
B) bowed away from the origin
C) does not intersect another indifference curve
D) a lower one is preferred to a higher one
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When we derive the demand curve for a good,we should remember that the
A) income effect must be greater than the substitution effect.
B) substitution effect must be greater than the income effect.
C) substitution effect must be in the same direction as the income effect.
D) income effect and the substitution effect may work in the same or in opposite directions.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-7
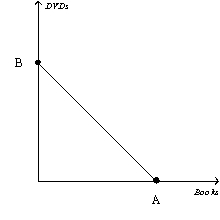 -Refer to Figure 21-7.Suppose a consumer has $200 in income,the price of a book is $5,and the price of a DVD is $10.What is the value of B?
-Refer to Figure 21-7.Suppose a consumer has $200 in income,the price of a book is $5,and the price of a DVD is $10.What is the value of B?
A) 40
B) 20
C) 10
D) 2
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer who doesn't spend all of her income
A) would be at a point outside of her budget constraint.
B) would be at a point inside her budget constraint.
C) must not be consuming positive quantities of all goods.
D) must be consuming at a point where her budget constraint touches one of the axes.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect substitutes,the
A) indifference curve is a downward-sloping straight line.
B) marginal rate of substitution is constant.
C) indifference curve is a vertical straight line.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-1
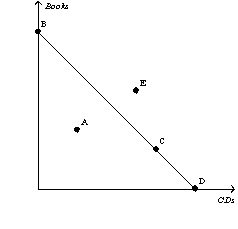 -Refer to Figure 21-1.Which point in the figure showing a consumer's budget constraint represents the consumer's income divided by the price of a CD?
-Refer to Figure 21-1.Which point in the figure showing a consumer's budget constraint represents the consumer's income divided by the price of a CD?
A) point A
B) point C
C) point D
D) point E
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following diagram shows one indifference curve representing the preferences for goods X and Y for one consumer. 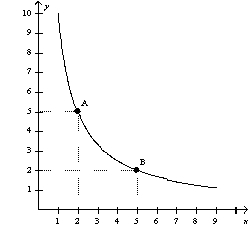 What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?
What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?
A) 2/5
B) 1
C) 5/2
D) 3
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw a budget constraint that is consistent with the following prices and income. Income = 200 PY = 50 PX = 25 a.Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if income increases to 500. b.Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if PY decreases to 20. c.Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if PX increases to 40.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect complements,the indifference curve is
A) a horizontal straight line.
B) bowed outward.
C) a downward-sloping straight line.
D) a right angle.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When indifference curves are downward sloping,the marginal rate of substitution is usually constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a consumer spends her income on two goods: music CDs and DVDs.The price of a CD is $8,and the price of a DVD is $20.If we graph the budget constraint by measuring the quantity of CDs purchased on the horizontal axis and the quantity of DVDs on the vertical axis,what is the slope of the budget constraint?
A) -5.0
B) -2.5
C) -0.4
D) The slope of the budget constraint cannot be determined without knowing the income the consumer has available to spend on the two goods.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 462
Related Exams