A) $3.33
B) $5
C) $15
D) $30
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-19
The following graph illustrates a representative consumer's preferences for marshmallows and chocolate chip cookies:
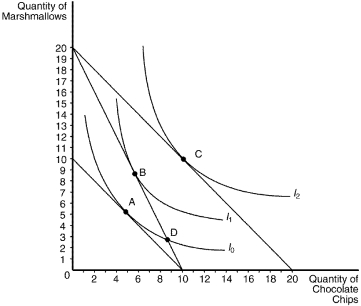 -Refer to Figure 21-19.Assume that the consumer has an income of $100 and currently optimizes at bundle A.When the price of marshmallows decreases to $5,which bundle will the optimizing consumer choose?
-Refer to Figure 21-19.Assume that the consumer has an income of $100 and currently optimizes at bundle A.When the price of marshmallows decreases to $5,which bundle will the optimizing consumer choose?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-5
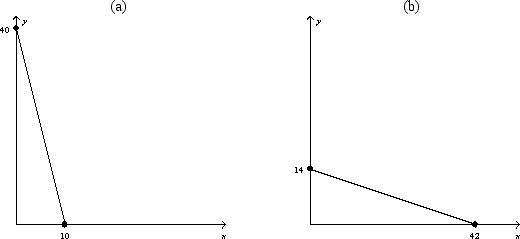 -Refer to Figure 21-5.In graph (b) ,what is the price of good X relative to good Y (i.e.,Pₓ/Pᵧ) ?
-Refer to Figure 21-5.In graph (b) ,what is the price of good X relative to good Y (i.e.,Pₓ/Pᵧ) ?
A) 1/3
B) 1
C) 3
D) 10
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the interest rate rises,an individual could choose to
A) increase consumption when young.
B) increase consumption when old.
C) decrease consumption when young.
D) Any of the above could be correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists represent a consumer's preferences using
A) demand curves.
B) budget constraints.
C) indifference curves.
D) supply curves.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of an inferior good decreases,
A) both the income and substitution effects encourage the consumer to purchase more of the good.
B) both the income and substitution effects encourage the consumer to purchase less of the good.
C) the income effect encourages the consumer to purchase more of the good, and the substitution effect encourages the consumer to purchase less of the good.
D) the income effect encourages the consumer to purchase less of the good, and the substitution effect encourages the consumer to purchase more of the good.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose at the consumer's current consumption bundle the marginal rate of substitution of cheese for wine is 1/2 bottle of wine per pound of cheese.The price of one pound of cheese is $6,and the price of a bottle of wine is $10.The consumer should increase his consumption of
A) cheese, decrease his consumption of wine, and move to a lower indifference curve.
B) cheese, decrease his consumption of wine, and move to a higher indifference curve.
C) wine, decrease consumption of cheese, and move to a higher indifference curve.
D) cheese, decrease consumption of wine, and remain on the same indifference curve.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two economists found empirical evidence that when the price of rice decreased in the Hunan province of China,local residents consumed less rice than before the price decrease.The study provides a real-world example of a(n)
A) normal good.
B) inferior good that is not a Giffen good.
C) Giffen good.
D) luxury good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the only two goods that Brett consumes are wine and cheese.When wine sells for $10 a bottle and cheese sell for $10 a pound,he buys 6 bottles of wine and 4 pounds of cheese - spending his entire income of $100.One day the price of wine falls to $5 a bottle and the price of cheese increases to $20 a pound,while his income does not change.The bundle of wine and cheese that he purchased at the old prices now costs
A) the same amount at the new prices.
B) less than Brett's income at the new prices.
C) more than Brett's income at the new prices.
D) We do not have enough information to answer the question.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bundle L contains 10 units of good X and 20 units of good Y.Bundle M contains 8 units of good X and 21 units of good Y.The consumer is indifferent between bundle L and bundle M.Assume that the consumer's preferences satisfy the four properties of indifference curves.Which of the following correctly expresses the marginal rate of substitution of good X for good Y between these two points?
A) The consumer will give up 1 unit of good X to gain 2 units of good Y.
B) The consumer will give up 2 units of good X to gain 1 unit of good Y.
C) The price of good X is twice as large as the price of good Y.
D) The price of good X is half as large as the price of good Y.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution is
A) the slope of a budget constraint.
B) always constant.
C) the slope of an indifference curve.
D) the point at which the budget constraint and the indifference curve are tangent.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of a good increases,all else equal,the higher price
A) reduces the consumer's set of buying opportunities.
B) leads to a parallel shift of the budget constraint.
C) will necessarily lead to an increase in the consumption of goods whose price did not change.
D) generally discourages the consumption of inferior goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw indifference curves that reflect the following preferences. a.pencils with white erasers and pencils with pink erasers b.left shoes and right shoes c.potatoes and rice d.income and polluted water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Phil's income increases,he purchases fewer spaghetti dinners than he did before his income increased.For Phil,spaghetti dinners are a(n)
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) optimal good.
D) luxury good.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The substitution effect from an increase in wages is evident in a
A) decrease in labor demand.
B) desire to consume less leisure.
C) desire to consume more leisure.
D) backward-bending labor supply curve.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A typical indifference curve is upward sloping.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Graphically demonstrate the conditions associated with a consumer optimum.Carefully label all curves and axes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the relative price of a concert ticket is three times the price of a meal at a good restaurant,then the opportunity cost of a concert ticket can be measured by the
A) slope of the budget constraint.
B) slope of an indifference curve.
C) marginal rate of substitution.
D) income effect.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The indifference curves for perfect substitutes are right angles.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-13
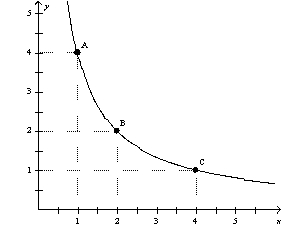 -Refer to Figure 21-13.As the consumer moves from A to B to C,the marginal rate of substitution
-Refer to Figure 21-13.As the consumer moves from A to B to C,the marginal rate of substitution
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains constant.
D) first increases, then decreases.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 462
Related Exams