A) Group 1: average annual premium increases
Group 2: average annual premium increases
B) Group 1: average annual premium decreases
Group 2: average annual premium increases
C) Group 1: average annual premium increases
Group 2: average annual premium decreases
D) Group 1: average annual premium decreases
Group 2: average annual premium decreases
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-5 Three candidates, Fred, Barb, and William, are running for office. There are three voters in the upcoming election: Heather, Don, and Luanne. Heather prefers Barb over Fred and Fred over William. Don prefers William over Barb and Barb over Fred. Luanne prefers Fred over Barb and Barb over William. -Refer to Scenario 22-5.If the voters were given a choice of Fred versus Barb first,then the winner was in a second election versus William,who would win?
A) Fred
B) Barb
C) William
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would violate transitivity?
A) John likes A more than B, C more than B, and C more than a.
B) Steve likes C more than B, A more than B, B more than D, and C more than D.
C) Sarah likes C more than A, B more than D, A more than B, and D more than C.
D) Mitch likes C more than B, C more than D, and B more than D.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classic example of adverse selection is the
A) market for used cars.
B) market for new houses.
C) relationship between husband and wife.
D) relationship between a worker and his employer.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The problem that arises when one person performs a task on behalf of another person is called
A) the hidden characteristics problem.
B) the lemons problem.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The tendency of many people to procrastinate supports the view that people are consistent over time.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When new professors are hired,their job performance is monitored closely.If they meet their institution's standards,they will eventually receive tenure.After receiving tenure,professors' job performance is less closely monitored,and they become difficult to fire.Tenure thus creates
A) adverse selection.
B) a Condorcet paradox.
C) a screening problem.
D) moral hazard.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evidence from experiments in which real people play the ultimatum game supports the idea that people
A) are rational wealth-maximizers.
B) tend to be driven by fairness, without regard for their own self-interest.
C) are driven by both fairness and self-interest.
D) have trouble calculating their own levels of wealth.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Arrow impossibility theorem shows that
A) democracy should be abandoned as a form of government.
B) it is impossible to improve upon democratic voting methods as a mechanism for social choice.
C) all voting systems are flawed as a mechanism for social choice.
D) the median voter's preferences will always win in a two-way vote.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-6
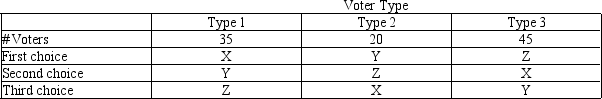 -Refer to Table 22-6.The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: X,Y,and Z.If a Borda count election were held among these voters,giving three points to each voter's first choice,two points to the second choice,and one point to the last choice,which outcome would win the election?
-Refer to Table 22-6.The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: X,Y,and Z.If a Borda count election were held among these voters,giving three points to each voter's first choice,two points to the second choice,and one point to the last choice,which outcome would win the election?
A) Outcome X
B) Outcome Y
C) Outcome Z
D) Either outcome X or outcome Z since these have the same total score.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economic models incorporate the assumption of rational behavior on the part of economic actors.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists assume that people are rational,they assume that
A) consumers maximize profits.
B) firms maximize revenues.
C) consumers maximize utility.
D) firms maximize output.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet paradox shows that
A) allocations of resources based on majority rule are always inefficient.
B) problems in counting votes can negate legitimate democratic outcomes.
C) the order on which things are voted can affect the result.
D) transitive preferences are inconsistent with rationality.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The principal-agent problem is more serious in large firms than in small firms because
A) monitoring employee activity in large firms is generally more difficult.
B) employees in large firms have less information.
C) profits increase with the size of the firm.
D) customers expect better treatment from small firms and they usually get it.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Students of microeconomic principles often say they are going to study "tonight," because the only way to pass the exam is to study some every night.When "tonight" comes,some students choose to do something else.Come exam-day,these students do not do well on their exam.This observation is an example of how people
A) are inconsistent over time.
B) are consistent over time.
C) are mainly interested in fairness.
D) are rational.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Signaling" refers to actions by an informed party for the sole purpose of
A) telling another party that the signaler has information to reveal, without actually revealing that information.
B) conveying false information.
C) confusing another party.
D) credibly revealing private information.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-5
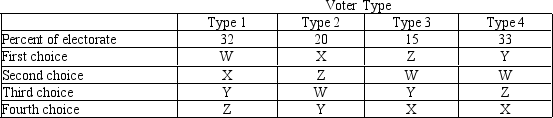 -Refer to Table 22-5.The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: W,X,Y,and Z.In addition,the table shows the percentage of voters of each type.Suppose a Borda count election is held in which each voter ranks the four outcomes,giving 1 point to last place,2 points to second to last,3 points to the second best,and 4 points to the best.In this case,which outcome would win?
-Refer to Table 22-5.The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: W,X,Y,and Z.In addition,the table shows the percentage of voters of each type.Suppose a Borda count election is held in which each voter ranks the four outcomes,giving 1 point to last place,2 points to second to last,3 points to the second best,and 4 points to the best.In this case,which outcome would win?
A) W
B) X
C) Y
D) Z
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-5
 -Refer to Table 22-5.The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: W,X,Y,and Z.In addition,the table shows the percentage of voters of each type.Based on this information,which of the following statements is false?
-Refer to Table 22-5.The table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible outcomes: W,X,Y,and Z.In addition,the table shows the percentage of voters of each type.Based on this information,which of the following statements is false?
A) Outcome W is preferred to outcome X overall.
B) Outcome X is preferred to outcome Y overall.
C) Outcome Y is preferred to outcome W overall.
D) Outcome W is preferred to outcome Z overall.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a principal-agent relationship?
A) Car dealer and potential customer
B) Business consultant and client
C) Retail store manager and potential customer
D) Both A and C are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Majority rule will produce the outcome most preferred by the median voter.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 199
Related Exams