A) unemployed and in the labor force.
B) unemployed, but not in the labor force.
C) in the labor force, but not unemployed.
D) neither in the labor force nor unemployed.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most people rely primarily on income other than their labor earnings to maintain their standard of living.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) There is consensus among economists that unions are good for the economy.
B) There is consensus among economists that unions are bad for the economy.
C) There is consensus among economists that, on net, unions have almost no impact on macroeconomic variables.
D) There is no consensus among economists about whether unions are good or bad for the economy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Structural unemployment is often thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm might offer efficiency wages so its workers will eat a more nutritious diet and therefore be healthier and more productive.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
About what percentage of jobs are destroyed every year and about what percentage of workers leave their jobs in a typical month?
A) 1% and 5%
B) 5% and 1%
C) 3% and 10%
D) 10% and 3%
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The unemployment that results from the process of matching workers and jobs is called frictional unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that appliance factory workers and furniture factory workers are not unionized. If the furniture factory workers unionize, then
A) the wages of appliance factory workers will rise and the wages of furniture factory workers will fall.
B) the wages of furniture factory workers will rise and the wages of appliance factory workers will fall.
C) the wages of both appliance factory workers and furniture factory workers will rise.
D) the wages of both appliance factory workers and furniture factory workers will fall.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of efficiency wages explains why
A) setting wages at the equilibrium level may increase unemployment.
B) it may be in the best interest of firms to offer wages that are above the equilibrium level.
C) the most efficient way to pay workers is to pay them according to their skills.
D) it is efficient for firms to set wages at the equilibrium level.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Edgar is working part-time. Diane is on temporary layoff. Who is included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "employed" category?
A) only Edgar
B) only Diane
C) both Edgar and Diane
D) neither Edgar nor Diane
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported in 2005 that there were 53.23 million people over age 25 who had at least a bachelor's degree, 40.59 million of whom were employed and 0.98 million of whom were unemployed. What were the labor-force participation rate and the unemployment rate for this group?
A) 76.3% and 1.8%
B) 76.3% and 2.4%
C) 78.1% and 1.8%
D) 78.1% and 2.4%
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an explanation for the existence of structural unemployment?
A) efficiency wages
B) job search
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unions
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose some country had an adult population of about 46 million, a labor-force participation rate of 75 percent, and an unemployment rate of 8 percent. How many people were unemployed?
A) 2.54 million
B) 2.76 million
C) 3.68 million
D) 8 million
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the wage is kept above the equilibrium wage for any reason, the result is structural unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines the unemployment rate as the percentage of
A) those unemployed relative to those employed.
B) the labor force that is unemployed.
C) the adult population that is unemployed.
D) the adult population that is unemployed or not in the labor force.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some persons are counted as out of the labor force because they have made no serious or recent effort to look for work. However, some of these individuals may want to work even though they are too discouraged to make a serious effort to look for work. If these individuals were counted as unemployed instead of out of the labor force, then
A) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be higher.
B) the unemployment rate would be higher and the labor-force participation rate would be lower.
C) the unemployment rate would be lower and the labor-force participation rate would be higher.
D) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be lower.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rfer to Labor
Labor Force Statistics by Age.
Suppose people in the adult population in a small country are classified based on their age.
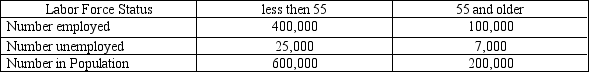 -Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age. In the proper order, which age group has the highest unemployment rate and which has the highest participation rate?
-Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age. In the proper order, which age group has the highest unemployment rate and which has the highest participation rate?
A) under 55, under 55
B) under 55, 55 and older
C) 55 and older, under 55
D) 55 and older, 55 and older
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions contribute to
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the demand for construction workers increased and the demands for textile and steel workers diminished. This is an example of
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The introduction of a union into an industry
A) creates a surplus of labor and so raises unemployment.
B) creates a surplus of labor and so reduces unemployment.
C) creates a shortage of labor and so raises unemployment.
D) creates a shortage of labor and so reduces unemployment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 562
Related Exams