A) Both labor supply and wages increase.
B) Labor supply increases, and wages decrease.
C) Labor supply decreases, and wages increase.
D) Both labor supply and wages increase
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an explanation for the existence of structural unemployment?
A) efficiency wages
B) job search
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unions
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People who are unemployed because of job search are best classified as
A) cyclically unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) frictionally unemployed.
D) discouraged workers.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following do unions not cause?
A) frictional unemployment
B) the wage to rise above the equilibrium level
C) conflict between insiders who benefit from high union wages and outsiders who do not get the union jobs
D) reduced wages in industries without unions
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-4 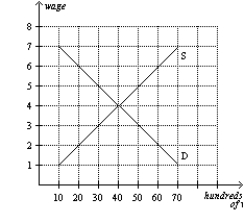 -Refer to Figure 28-4. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $7, how many workers will be unemployed?
-Refer to Figure 28-4. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $7, how many workers will be unemployed?
A) 0
B) 2,000
C) 4,000
D) 6,000
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2009, based on concepts similar to those used to estimate U.S. employment figures, the Swedish adult non- institutionalized population was 7.568 million, the labor force was 4.888 million, and the number of people employed was 4.486 million. According to these numbers, the Swedish labor-force participation rate and unemployment rate were about
A) 64.6% and 8.2%.
B) 64.6% and 5.3%.
C) 59.3% and 8.2%.
D) 59.3% and 5.3%.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Efficiency wages
A) may increase productivity.
B) will increase unemployment.
C) may improve worker health.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Job search
A) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health both create frictional unemployment.
B) creates frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health creates structural unemployment.
C) creates structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health creates frictional unemployment.
D) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health both create structural unemployment.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyclical unemployment
A) has a different explanation than does the natural rate of unemployment.
B) refers to the yeartoyear fluctuation in unemployment around an economy's natural rate of unemployment.
C) is closely associated with short-run ups and downs of economic activity.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a union bargains successfully with employers, in that industry,
A) both wages and unemployment increase.
B) wages increase and unemployment decreases.
C) wages decrease and unemployment increases.
D) both wages and unemployment decrease.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics divides the adult population into three categories: employed, unemployed, and not in the labor force.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the wage is above the equilibrium level,
A) the labor market is functioning more efficiently than it otherwise would function.
B) there is a shortage of labor.
C) the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded.
D) job search is the primary explanation for the unemployment that is observed.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The unemployed who quit their jobs, were fired for cause, or just entered the labor force are eligible for unemployment insurance.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Within the U.S. population, teenagers ages 16-19) have similar rates of unemployment than adults of prime working age ages 25-54), regardless of race or gender.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the minimum wage is currently above the equilibrium wage, then a decrease in the minimum wage
A) increases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
B) decreases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
C) increases the quantity of labor demanded but decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
D) decreases the quantity of labor demanded but increases the quantity of labor supplied.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-6
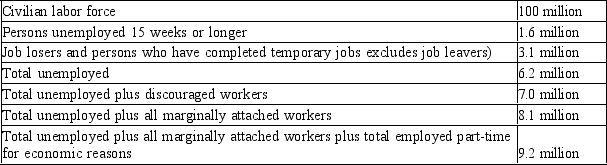 -Refer to Table 28-6. What is the U-2 measure of labor underutilization?
-Refer to Table 28-6. What is the U-2 measure of labor underutilization?
A) 1.5%
B) 3.1%
C) 4.7%
D) 6.2%
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most spells of unemployment are
A) long, and most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
B) long, but most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
C) short, but most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
D) short, and most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the theory of efficiency wages, firms operate more efficiently if wages are below the equilibrium level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-2
Labor Data for Aridia
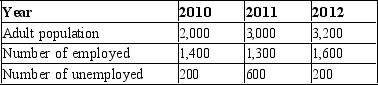 -Refer to Table 28-2. The labor force of Aridia in 2011 was
-Refer to Table 28-2. The labor force of Aridia in 2011 was
A) 1,300.
B) 1,900.
C) 2,400.
D) 3,000.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Frictional unemployment is inevitable because the economy is always changing.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 461 - 480 of 698
Related Exams