A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sizable economic profits can persist over time under monopoly if the monopolist
A) produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B) is protected by barriers to entry.
C) operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D) earns revenues that exceed variable costs.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly market
A) always maximizes total economic well-being.
B) always minimizes consumer surplus.
C) generally fails to maximize total economic well-being.
D) generally fails to maximize producer surplus.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not one of the ways that antitrust laws promote competition?
A) Antitrust laws allow the government to prevent mergers.
B) Antitrust laws allow the government to break up companies into smaller ones.
C) Antitrust laws prevent companies from coordinating their activities in ways that make markets less competitive.
D) Antitrust laws allow the government to shut down any firm the government believes has monopoly power.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 15-25 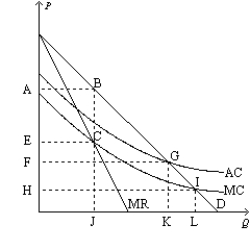 -Refer to Figure 15-25. If a regulator requires this firm to charge a socially optimal price, how much deadweight loss results?
-Refer to Figure 15-25. If a regulator requires this firm to charge a socially optimal price, how much deadweight loss results?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-6 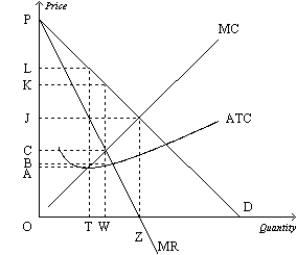 -Refer to Figure 15-6. What price will the monopolist charge?
-Refer to Figure 15-6. What price will the monopolist charge?
A) A
B) C
C) K
D) L
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a monopolist charges a price of $27 for its product and sells 10 units at that price. At 10 units of production the firm has average fixed cost equal to $10 and average variable cost equal to $12. How much total profit is the firm earning at this price?
A) $5
B) $25
C) $50
D) $140
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopoly pricing prevents some mutually beneficial trades from taking place. These unrealized, mutually beneficial trades are
A) not a concern if a market is perfectly competitive.
B) a deadweight loss to society.
C) a function of the reduction in the quantity produced by a monopolist in comparison to a competitive market.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopoly occurs when
A) the product is sold in its natural state, such as water or diamonds.
B) there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C) the firm is characterized by a rising marginal cost curve.
D) production requires the use of free natural resources, such as water or air.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) The demand curve facing a competitive firm is perfectly elastic.
B) The demand curve facing a monopolist is the market demand curve.
C) A monopolist can charge any price and sell any quantity that it chooses.
D) A monopolist can alter the market price by adjusting the quantity that it produces.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly firm,
A) price always equals marginal revenue.
B) price always exceeds average revenue.
C) any price-quantity combination will maximize profits.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to the monopoly outcome with a single price, imperfect price discrimination i) sometimes raises total surplus. Ii) sometimes lowers total surplus. Iii) always leads to a lower quantity of output.
A) i) and ii) only
B) ii) and iii) only
C) i) and iii) only
D) i) , ii) , and iii)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a downward-sloping market demand curve, its
A) average revenue is less than the price of the product.
B) average revenue is less than marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue is less than the price of the product.
D) marginal revenue is greater than the price of the product.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fundamental cause of monopoly is
A) incompetent management in competitive firms.
B) the zero-profit feature of long-run equilibrium in competitive markets.
C) advertising.
D) barriers to entry.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of $20, produces an output level of 100 units, and charges a price of $50. The socially efficient level of output is 200 units. Assume that the demand curve and marginal revenue curve are the typical downward-sloping straight lines. The monopoly deadweight loss equals $1,500.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-4 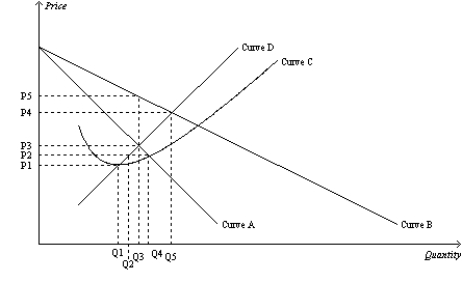 -Refer to Figure 15-4. Profit can always be increased by increasing the level of output by one unit if the monopolist is currently operating at i) Q1.
Ii) Q2.
Iii) Q3.
Iv) Q4.
-Refer to Figure 15-4. Profit can always be increased by increasing the level of output by one unit if the monopolist is currently operating at i) Q1.
Ii) Q2.
Iii) Q3.
Iv) Q4.
A) ii) only
B) i) or ii) only
C) i) only
D) i) , ii) , or iii) only
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist earns higher profits by charging one price than by practicing price discrimination.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Financial aid to college students, quantity discounts, and senior citizen discounts are all examples of
A) consumer surplus.
B) deadweight loss.
C) price discrimination.
D) nonprofit pricing strategies.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because a monopolist is the sole producer in its market, it can necessarily alter the price of its good i) without affecting the quantity sold. Ii) without affecting its average total cost. Iii) by adjusting the quantity it supplies to the market.
A) ii) only
B) iii) only
C) i) and ii) only
D) ii) and iii) only
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The De Beers Diamond company advertises heavily to promote the sale of all diamonds, not just its own. This is evidence that it has a monopoly position to some degree.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 361 - 380 of 637
Related Exams