A) there would be no crowding out.
B) the full multiplier effect of the increase in government purchases would be realized.
C) the AD curves that actually apply, before and after the change in government purchases, would be separated horizontally by the distance equal to the multiplier times the change in government purchases.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If households view a tax cut as temporary, then the tax cut
A) has no effect on aggregate demand.
B) has more of an effect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
C) has the same effect as when households view the cut as permanent.
D) has less of an effect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes argued that
A) irrational waves of pessimism cause decreases in aggregate demand and increases in unemployment.
B) irrational waves of optimism cause decreases in aggregate demand and decreases in aggregate supply.
C) changes in business and consumer expectations generally stabilize the economy.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government buys new weapons systems. The manufacturers of weapons pay their employees. The employees spend this money on goods and services. The firms from which the employees buy the goods and services pay their employees. This sequence of events illustrates
A) the accelerator effect.
B) the multiplier effect.
C) the chain effect.
D) the bandwagon effect.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC is 5/6 then the multiplier is
A) 6/5, so a $200 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $240.
B) 5, so a $200 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $1000.
C) 6, so a $200 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $1200.
D) 6/5, so a $200 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $1200.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in the interest rate
A) shift aggregate demand whether they are caused by changes in the price level or by changes in fiscal or monetary policy.
B) shift aggregate demand if they are caused by changes in the price level, but not if they are caused by changes in fiscal or monetary policy.
C) shift aggregate demand if they are caused by fiscal or monetary policy, but not if they are caused by changes in the price level.
D) do not shift aggregate demand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, equilibrium in the money market is achieved by adjustments in
A) the price level.
B) the interest rate.
C) the exchange rate.
D) real wealth.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term crowding-out effect refers to
A) the reduction in aggregate supply that results when a monetary expansion causes the interest rate to decrease.
B) the reduction in aggregate demand that results when a monetary expansion causes the interest rate to decrease.
C) the reduction in aggregate demand that results when a fiscal expansion causes the interest rate to increase.
D) the reduction in aggregate demand that results when a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes causes the interest rate to increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed buys government bonds, the reserves of the banking system
A) increase, so the money supply increases.
B) increase, so the money supply decreases.
C) decrease, so the money supply increases.
D) decrease, so the money supply decreases.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An decrease in taxes shifts aggregate demand
A) to the right. The larger the multiplier is, the farther it shifts.
B) to the right. The larger the multiplier is, the less it shifts.
C) to the left. The larger the multiplier is, the farther it shifts.
D) to the left. The larger the multiplier is, the less it shifts.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the multiplier has a value that exceeds 1, and there are no crowding out or investment accelerator effects. Which of the following would shift aggregate demand to the right by more than the increase in expenditures?
A) an increase in government expenditures
B) an increase in net exports
C) an increase in investment spending
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the inflation rate is zero, then the nominal and real interest rate are the same.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of liquidity preference, an increase in the price level causes the
A) interest rate and investment to rise.
B) interest rate and investment to fall.
C) interest rate to rise and investment to fall.
D) interest rate to fall and investment to rise.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In liquidity preference theory, an increase in the interest rate, other things the same, decreases the quantity of money demanded, but does not shift the money demand curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Last year, total income increased $1,000 and consumption increased $800. An increase in government spending equal to $10 would cause output to increase by $_____ because the multiplier is ______.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier is 6, then the MPC is
A) 0.16.
B) 0.83.
C) 0.71.
D) 0.86.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sequences best represents the crowding-out effect?
A) government purchases ↑ ⇒ GDP ↑ ⇒ supply of money ↓ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
B) government purchases ↓ ⇒ GDP ↓ ⇒ demand for money ↓ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↓ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
C) government purchases ↑ ⇒ GDP ↑ ⇒ demand for money ↑ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
D) taxes ↑ ⇒ GDP ↓ ⇒ demand for money ↓ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 34-4. On the figure, MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand. 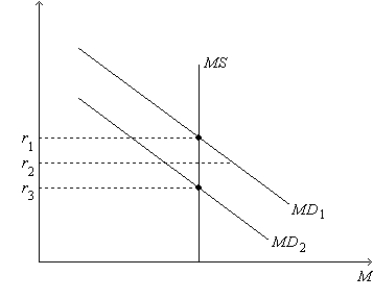 -Refer to Figure 34-4. Suppose the money-demand curve is currently MD1. If the current interest rate is r2, then
-Refer to Figure 34-4. Suppose the money-demand curve is currently MD1. If the current interest rate is r2, then
A) the quantity of money that people want to hold is less than the quantity of money that the Federal Reserve has supplied.
B) people will respond by selling interest-bearing bonds or by withdrawing money from interest-bearing bank accounts.
C) bond issuers and banks will respond by lowering the interest rates they offer.
D) in response, the money-demand curve will shift rightward from its current position to establish equilibrium in the money market.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sequences best explains the negative slope of the aggregate-demand curve?
A) price level ↑ ⇒ demand for money ↑ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
B) price level ↑ ⇒ demand for money ↓ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
C) price level ↓ ⇒ demand for money ↓ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
D) price level ↑ ⇒ equilibrium interest rate ↑ ⇒ demand for money ↑ ⇒ quantity of goods and services demanded ↓
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is likely that a constitutional amendment that required the government always to run a balanced budget would
A) contribute to a more stable level of output.
B) mitigate the crowding-out effect.
C) eliminate the economy's automatic stabilizers.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 511
Related Exams